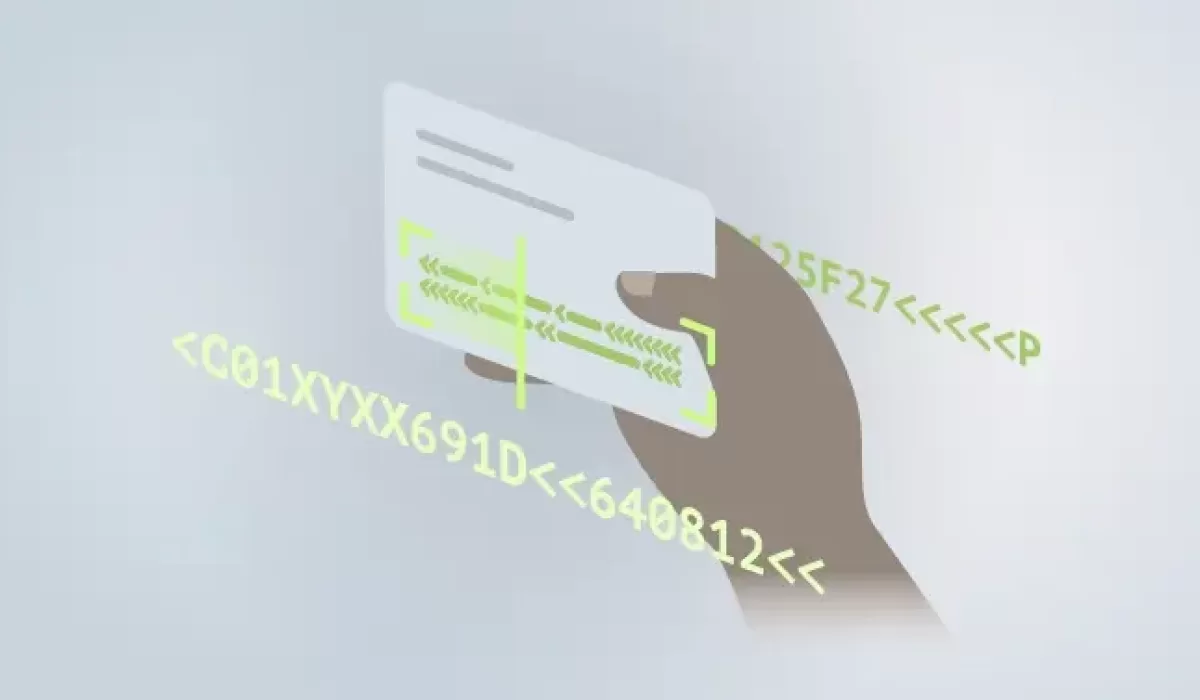
The Machine Readable Zone (MRZ) is a crucial element on passports and ID cards, encoding personal information for fast and accurate machine reading. This zone helps verify identities, enhance security, and streamline processes at borders and checkpoints.
What is the Machine Readable Zone (MRZ)?
The machine readable zone is a mandatory element of identity documents designed for machine reading to enhance the verification process. Its primary purpose is to verify identity and prevent unauthorized access by securely encoding vital information. The MRZ consists of two or three lines of text, including the document holder’s name, date of birth, and expiration date, all written in a machine-readable format.
The MRZ was standardized under ICAO Document 9303 to provide a common framework for machine-readable documents, first added to passports in 1980. The development of machine readable travel documents began in the late 1960s, paving the way for modern MRZ implementation. The introduction of MRZ technology facilitates quick and secure reading and verification, improving the overall effectiveness of identity verification systems.
One of the significant advantages of MRZ over manual verification methods is its efficient design, allowing machines to read and process personal data quickly. Standardization of MRZ codes enhances data retrieval processes by ensuring consistent capture of personal information across various documents.
Key features of MRZ
The MRZ encodes critical personal information, including the document holder’s name, nationality, date of birth, passport number, gender, and passport expiration date. This standardized presentation of data ensures that machines read MRZ codes accurately and consistently across different documents.
The MRZ employs a specific font, OCR-B, to facilitate machine reading. Additionally, check digits are included to enhance data verification, preventing forgery and ensuring the integrity of the information. Security features such as checksums and syntactic guidelines are embedded in MRZ codes to prevent forgery.
Importance of MRZ
The MRZ enhances security in identity verification by making alterations and forgeries harder, thus speeding up identity checks. It helps verify document authenticity through checksums and encoded data, effectively detecting fraud. The high level of security in MRZ codes makes them hard to forge or manipulate, thereby protecting personal information.
One of the most significant benefits of MRZ is its efficiency. By presenting personal information in a structured format, MRZ reduces manual processing and human error, leading to a more efficient verification process. Presenting data in a structured manner is key to efficient and accurate digital onboarding.
Types of Machine Readable Zones

There are three types of MRZ used for identity documents, each tailored to specific needs. These include formats ID1, ID2, and ID3, which vary based on the document type. The MRZ format includes details such as document type, holder’s name, document number, nationality, birth date, sex, and expiration date, as well as the identity document.
Each of these types is designed to fit different identity documents like passports, ID cards, and visas. The specific details encoded in the MRZ, such as document type and personal information, make it easier for machines to read and verify identity documents accurately.
Type 1 MRZ: National Identity Cards
Type 1 MRZ comprises three lines of 30 characters each. National identity cards use it for automated identity verification. The standardized format of Type 1 MRZ ensures that the encoded information is consistently readable across different identity documents.
Type 1 MRZ plays a crucial role in preventing identity fraud by securely encoding personal information. This type of MRZ is also used in other identity documents such as driver’s licenses and vehicle registration certificates, making it a versatile tool in identity verification processes.
Type 2 MRZ: Travel Documents
Type 2 MRZ is primarily utilized in visas and consists of two lines of 36 characters each. Countries like Romania and France use this format, ensuring a consistent and secure method for encoding travel document information. The MRZ encoding in travel documents is crucial to prevent issues during applications and travel, such as passing airport security.
The structured format of Type 2 MRZ makes it easier for machines to read and verify the encoded data, enhancing security and efficiency in the processing of travel documents. This type of MRZ is also used in other identity documents, ensuring a standardized approach to identity verification across different countries.
Type 3 MRZ: Machine-Readable Passports
Type 3 MRZ, used in passports, consists of two lines of 44 characters each. It is specifically designed to meet international standards for passports and contains encoded personal data such as the holder’s name, nationality, and passport number. The ‘P’ indicator in an MRZ code signifies that the document type is a passport.
This type of MRZ ensures that passport information is consistently readable across different countries, enhancing global travel security. The standardized format of Type 3 MRZ makes it easier for machines to read and verify passport data, reducing the risk of human error and improving the efficiency of border control processes, including the machine readable passport.
How Machines Read MRZ Codes
The process of reading MRZ codes begins with scanning the ID document. Optical character recognition (OCR) technology reads the printed characters on the MRZ code, enabling machines to interpret the data. Higher quality images improve the algorithms’ ability to find and extract MRZ data accurately.
Capturing and Scanning MRZ
Capturing MRZ data involves scanning the MRZ and saving its content in an electronic format. Optical scanners play a vital role in reading the MRZ by capturing the image of the MRZ for further processing.
Devices like mobile scanners utilize OCR for precise reading, ensuring that the encoded data is accurately captured.
Data Extraction from MRZ
Recognition and extraction of embedded text are crucial in the MRZ data extraction process. After capturing the MRZ, data is recognized and extracted using OCR systems. The data extracted from the MRZ includes critical personal identifiers, which are then converted into a structured format, ensuring accurate identity verification.
Parsers play a role in detecting standard MRZ types or non-standard ones during the processing of the data. This step ensures that the MRZ data is accurately interpreted and can be reliably used for identity verification and other processes.
Verification of Extracted Data
The verification of extracted data involves comparing calculated checksums with original checksums to ensure data accuracy. Check digits follow almost every data set in the MRZ, providing a method to validate specific data portions using the ICAO algorithm. This process helps in confirming the validity of document numbers in the MRZ.
Visual inspection serves as an additional method to verify MRZ data, complementing electronic checks. Factors such as the meanings of characters, parameters, and their placement are critical in the verification of MRZ data, ensuring that the information is accurate and reliable.
Role of MRZ in Identity Verification
The MRZ is a critical security feature in identity documents like passports, enhancing machine reading and verification, as well as security, efficiency, and reliability in identity verification processes. Recent advancements have made MRZ technology improve accuracy in verifying identity documents and minimize human error.
Exposing MRZ details can lead to serious identity theft incidents due to the sensitive nature of the data encoded. To make the verification process faster and more effective, robust MRZ recognition technology is essential.
Travel and Border Control
MRZ codes streamline the identity verification process, allowing for rapid checks at borders and in various business sectors. This technology accelerates ID verification at various checkpoints, ensuring quick and accurate identification. It also enhances security measures at border checkpoints by providing quick access to traveller information.
Artificial intelligence in MRZ verification can improve reading accuracy even under suboptimal conditions, such as poor lighting or damaged documents. The presence of MRZ significantly reduces the potential for human error during document checks, making the process more efficient and reliable.
Financial Institutions
The use of MRZ in financial institutions helps in compliance with regulations by facilitating identity verification of customers. Monitoring where MRZ data is shared can help in spotting potential identity theft. AI systems can perform complex analyses of MRZ data, leading to higher accuracy in identifying fraudulent documents.
Innovations in MRZ technology are expected to further enhance fraud detection and data security through advanced image recognition techniques. The integration of advanced machine learning algorithms in MRZ technology is expected to revolutionize identity verification by further minimizing errors and processing time.
Healthcare Services
MRZ technology plays a crucial role in the healthcare sector by ensuring accurate patient identification. In healthcare, MRZ technology enhances patient identification, which is crucial for safe and effective treatment. It also facilitates secure data management, improving the overall handling of patient information.
Enhanced patient identification and data management through MRZ technology significantly improves healthcare service delivery and security. This ensures that patients receive the correct treatment and that their personal information is protected.
Protecting Personal Information in MRZ
Protecting personal identities is critical to ensure security against identity theft and fraud. Unauthorized exposure of MRZ information can lead to potential identity theft and misuse of personal data.
Securing MRZ information is crucial for preventing identity theft and ensuring personal data protection.
Risks of Publicly Posting MRZ
Publicly disclosing MRZ can result in unauthorized retrieval of personal information. The encoded data in MRZ contains sensitive personal identifiers that can be misused.
Securing MRZ information is critical to prevent identity theft and protect personal data.
Best Practices for MRZ Protection
Understanding MRZ contributes to online security by helping protect sensitive information. Verifying the legitimacy of organizations requesting MRZ data is necessary to protect personal information.
Ensuring compliance with international data protection standards and state-level regulations is vital for protecting MRZ information.
Advances in MRZ Technology
The MRZ was developed by the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) to standardize identity verification globally. Advances in MRZ technology have led to significant improvements in the accuracy and efficiency of identity verification.
These developments include enhanced scanning capabilities, faster data extraction methods, and improved security features in MRZ systems.
AI-Driven MRZ Verification
AI enhances the accuracy, speed, and security of MRZ verification. It improves efficiency in MRZ processing, significantly reducing wait times.
Artificial intelligence can detect fraud and analyze MRZ codes effectively, even in poor conditions.
Future Trends in MRZ Technology
The ongoing evolution of MRZ technology is expected to further streamline identity verification processes, making them more secure and efficient in the future. Recent developments include enhanced scanning capabilities, faster data extraction methods, and improved security features in MRZ systems.
AI-driven MRZ verification systems utilize artificial intelligence to increase the speed, accuracy, and security of data processing.
Last Thoughts
The Machine Readable Zone plays a pivotal role in modern identity verification, providing a secure and efficient method for encoding and reading personal information. From national identity cards to travel documents and machine-readable passports, MRZ technology has revolutionized the way we verify identities. With advancements in AI and future trends pointing towards even greater accuracy and security, the MRZ is set to remain at the forefront of identity verification. Understanding and protecting MRZ data is crucial in preventing identity theft and ensuring the integrity of personal information.



