Record keeping is an important part of Anti-Money Laundering (AML) compliance. It involves policies and practices for creating, organising, and managing information. These requirements, set by regulatory bodies or internally, ensure compliance with legal obligations. Firms must maintain records of customer identity and transactions, forwarding suspicious cases to law enforcement for investigation. Companies should keep appropriate records based on business complexity, scale, and nature, ensuring compliance with local regulations. Keeping records up-to-date involves effective communication with customers.
Record Keeping and Documentation Requirements
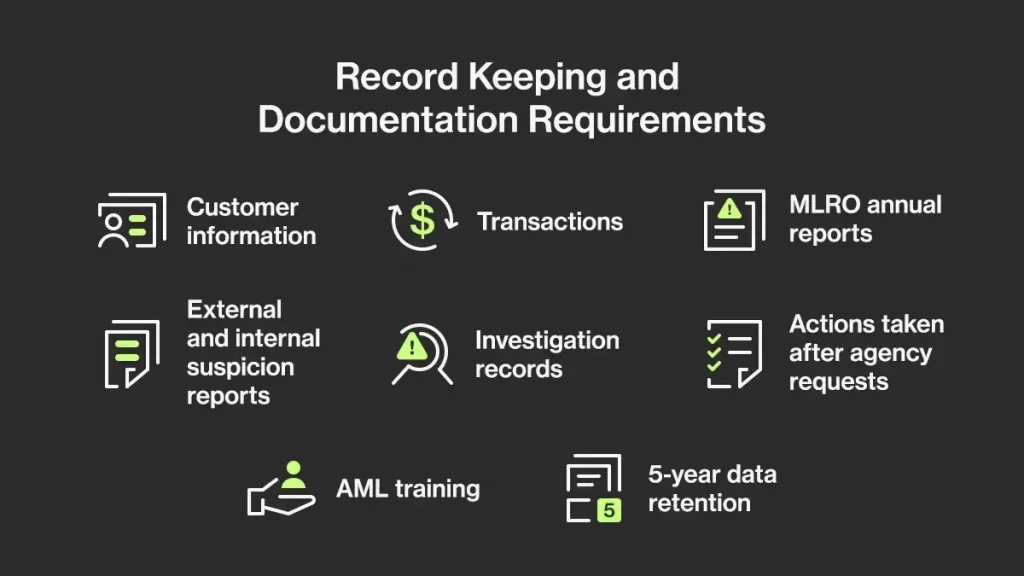
Anti-money laundering regulations mandate the retention of transaction records, encompassing credit and debit notes, checks, and correspondence throughout the business relationship. Firms must maintain an audit trail to compile financial profiles for suspicious accounts or customers. Organisations are obligated to prepare and keep records related to AML and Counter-Terrorist Financing (CTF) during the length of the business relationship as well as for 5 years after the end of the relationship.
- Customer information
- Transactions
- MLRO annual reports
- External and internal suspicion reports
- Investigation records
- Actions taken after agency requests
- AML training
Customer Information
This includes all information gathered during identity verification: Name, address, date of birth, photocopies of the provided identity document, as well as records of the identity verification process itself. In addition, this may include Politically Exposed Person (PEP) and sanctions status as well as any changes to the relevant information that were gathered during ongoing monitoring.
Transactions
In general, records must be kept of all transactions, with specific attention paid to large cash transactions, large virtual currency transactions, any transactions over specified reporting thresholds, electronic fund transfers, foreign currency exchange transactions, and records of the accounts.
Suspicion and Investigation Reports
Reporting suspicious activity is essential to preventing financial crime and requires extensive record-keeping of any suspicions as well as any investigations and their findings.
The Importance of Record-Keeping in AML Practices

Record-keeping is the backbone of any successful AML system. It serves as a comprehensive documentation system that not only ensures compliance with regulatory requirements but also acts as a valuable resource for internal investigations and audits. Here’s why it’s indispensable:
Regulatory Compliance:
In order to prevent money laundering and combat terrorist financing, AML regulations demand robust documentation of customer due diligence (CDD) processes, transaction monitoring, and suspicious activity reporting. Comprehensive records act as tangible evidence of compliance, proving a company adheres to legal and regulatory requirements.
Internal Investigations:
In the event of suspicious activities or potential money laundering, having well-maintained records facilitates swift and efficient internal investigations. This is crucial for identifying and mitigating risks promptly, protecting the institution’s reputation.
Audit Trail:
A thorough audit trail is essential for accountability and transparency. Properly maintained records provide a chronological sequence of actions, making it easier for auditors to verify compliance with AML policies and procedures.
Risk Assessment and Management:
Record-keeping aids in identifying patterns and trends, enabling financial institutions to assess and manage risks effectively. This proactive approach is vital in preventing and detecting money laundering activities before they escalate.
Mastering Record-Keeping Practices in AML
Now that we understand the significance of record-keeping in AML processes, let’s explore some best practices for mastering this critical aspect:
Centralised Documentation:
Establish a centralised repository for AML records. This ensures that all relevant information, including customer profiles, PEP and sanctions status, and risk assessments, is easily accessible and organised for efficient retrieval.
In order to help companies achieve this, Ondato offers a centralised hub solution, which gathers all relevant data in one place, creating client cards, making it easy to update any outdated information and double-check data. In addition, this information can be easily accessible by relevant employees that can leave internal comments and organise customers by their risk scores.
Ongoing Monitoring and Documentation:
Implement ongoing monitoring systems that automatically document transactions and activities. This not only streamlines the record-keeping process but also enhances the institution’s ability to identify and respond to suspicious activities promptly.
Regular Training and Updates:
Train relevant employees regularly on the importance of accurate record-keeping. Keeping staff informed about regulatory changes and updates ensures that they are equipped to adapt their practices to evolving AML requirements.
Data Security Measures:
Implement robust data security measures to protect sensitive AML information. This includes encryption, access controls, and regular security audits to safeguard against unauthorised access and data breaches.
Automation and Technology Integration:
Leverage automation and integrate advanced technologies, such as artificial intelligence and machine learning, especially during digital onboarding to enhance the accuracy and efficiency of record-keeping processes. These technologies can help identify patterns and anomalies that may go unnoticed with manual methods.
Final Thoughts
While record keeping and reporting may not boast glamour, they form the bedrock of business operations, particularly in the realm of AML compliance. Effective record-keeping not only acts as a shield against legal troubles but also establishes a sturdy foundation for internal processes and decision-making.
Regularly reassessing your record-keeping and reporting systems is imperative to ensure alignment with current regulatory standards. Opt for digital solutions and software to enhance efficiency, and remain vigilant in reporting any suspicious activities to avert severe consequences.