The rapidly rising rates of fraud have raised the stakes for financial institutions. It has been estimated that in 2021, on average, financial institutions were fined $34.4 million for AML (Anti-Money Laundering) related compliance breaches. The staggering financial loss comes from a failure to understand who these institutions are working with and prevent money laundering risks. That’s why Know Your Customer procedures have never been as important as they are now.
What is KYC?
Know Your Customer (KYC) is a set of regulatory procedures used to verify a customer’s identity and ascertain what fraud risk they may pose. Many financial institutions turn to KYC processes to assess money laundering risks.
KYC compliance has always been a concern for financial institutions like banks, online payment platforms, and insurance firms. However, they’re not the only ones that should care. The number of industries that must comply with KYC and perform customer due diligence is expanding. Organizations that provide healthcare, gambling, telecommunications, and many other services must prove Know Your Customer compliance as well.
Types of KYC
KYC can be divided into two main types: eKYC and in-person verification.
eKYC
eKYC is a digital KYC procedure, also known as an automatic identity verification process. It allows financial institutions to onboard clients in real time without compromising security. All necessary checks can be performed in the background with one customer identification program.
Various technologies can help to improve the eKYC process. Customers can save time with OCR mode, which automatically extracts information from their IDs. Liveness detection can ensure that a person is present during the process. Ongoing monitoring minimizes any future risk.
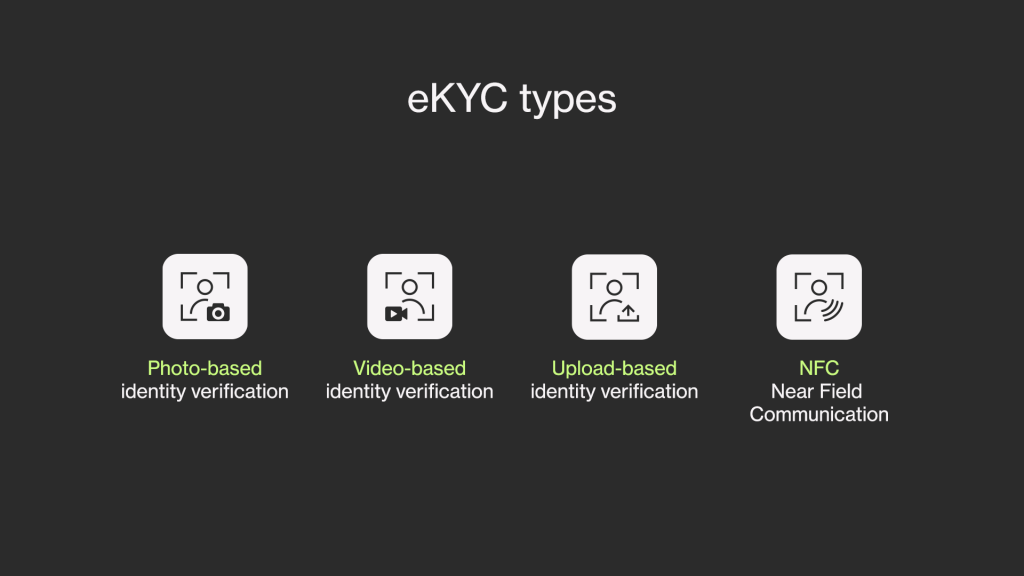
eKYC comes in several different types, such as:
Photo-based identity verification
Ensures a simple and familiar onboarding process for clients. While the steps a client has to take vary depending on local regulatory requirements, the Ondato solution onboards customers in 2 steps:
- They take a selfie. Then, the system performs a liveness check and maps out their biometric data.
- The client takes a picture of their document.
In the background of the process, the client’s data is checked against numerous ID registries to confirm its authenticity and KYC compliance. The process usually takes around 60 seconds.
Video-based identity verification
Provides an assisted identity verification in a real-time video call. A customer’s biometric and document data is captured during an encrypted call. The KYC specialist may ask further questions to ensure that the client is who they claim to be. The video call is analyzed for possible spoofing attempts, ensuring that no fraudster can fool the KYC specialist or the system. The process is completely secure and establishes a personal connection with the customer to enhance their experience with KYC processes.
Upload-based identity verification
Is a process that allows users to submit data manually. This method can be used when the KYC regulations allow the client to not be present during the verification process. It’s a standalone document verification solution that replaces real-time procedures while staying compliant with KYC requirements.
NFC (Near Field Communication)
Allows compatible devices to extract and wirelessly transfer data from microchips. It is used as an efficient security measure that provides fast customer onboarding by extracting the information from ID documents.
In-Person-Verification, or IPV, refers to a physical KYC process. A customer must physically deliver relevant KYC documents, such as their ID, proof of address, etc. The KYC specialist will run the data against various registries to confirm authenticity.
In-Person Verification KYC
In-Person-Verification, or IPV, refers to a physical KYC process. A customer must physically deliver relevant KYC documents, such as their ID, proof of address, etc. The KYC specialist will run the data against various registries to confirm authenticity.
In-Person-Verification versus Digital KYC
Long gone are the days when only a human could verify the authenticity of an ID. These days, technology can be just as effective. However, KYC regulations require financial institutions to combine these two types. Let’s discuss why that’s a good idea.
Price
The physical verification process requires much more resources, such as labour, office space, technology, training, etc.
The cost of a well-trained KYC specialists’ team tops the price of any software. For example, we have estimated that big banks in Germany, the Netherlands, France, and Switzerland spend an average of 5.7 million on KYC processes each year. 74% of this cost is dedicated to labour.
Implementing automated identity verification software can cut resources by more than half. A KYC check of one customer can cost less than €1 by using a solution like Ondato. The price can be even lower depending on the number of verifications you need to perform.
Processing Time
Onboarding time is crucial to customer satisfaction. That’s why it’s imperative to make the process as fast as possible to avoid losing clients. Traditional banks that still rely on many paper-based processes can take up to 18 minutes to complete a KYC check of a client. Meanwhile, depending on the process you choose, the Ondato system completes the process in under 90 seconds.
Another important aspect worth comparing is how many checks can be performed within a certain timeframe. In the traditional bank, on average, one specialist performs three checks per hour. In the meantime, Ondato verifies 50 users.
Success Rate
Human error is common in manual processes. Mistakes in the verification process can occur due to a lack of properly trained specialists, fatigue, and a lack of focus. That is why dedicating the entire process to humans is inefficient. It is critical to combine human input with technology to achieve the best results in customer due diligence.
The newest technological developments allow KYC technology to map out the biometric data of a customer’s face and ensure no spoofing artefacts, such as masks, are involved in the verification process. The technology also checks the document’s authenticity by efficiently spotting any alterations. All of this combined results in a 99.8% success rate.
What is the Difference Between KYC and KYB?
Know Your Customer and Know Your Business are similar concepts, yet they should not be confused. While both procedures are verification standards, they deal with different entities.
KYC applies to an individual, such as a person trying to open a bank account. They protect financial institutions against money laundering, corruption and fraud from their individual clients. This process requires several steps to understand the nature of customer activity, establish identity and ensure their funds are legitimate.
Meanwhile, KYB checks are performed on business organizations. This involves the due diligence review of any business that a company works with. KYB processes establish the company’s identity and authenticity to ensure AML compliance.
What Is the KYC Process?
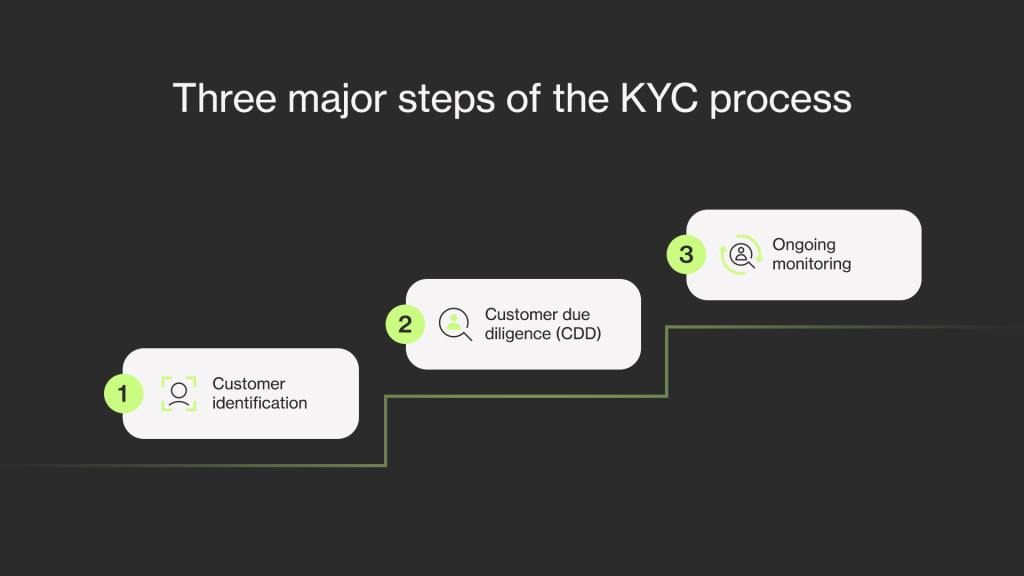
The KYC process involves three major steps:
- Customer identification: a customer’s identity is verified by checking the provided documents during this step.
- Customer due diligence (CDD): a process that involves the collection of all needed data about the customer. The data is gathered from verified and reputable sources to analyze the risk factors of the customer. Full compliance is ensured by taking additional steps:
- PEP screening: a customer’s name is checked against the politically exposed person lists to evaluate their risk score. According to international standards, a person involved in politics is deemed to be more susceptible to corruption. Thus, their risk score is higher.
- Sanctions screening: a customer is checked to ensure that they do not appear on a sanctioned entity list.
- Adverse media screening: a customer’s reputation is reviewed by scanning through media outlets.
- If these checks result in a higher risk score, Enhanced due diligence (EDD) should be performed. For example, high risk is assigned to politically exposed persons or those from high-risk countries. A deep investigation is performed on a customer during the process to evaluate possible fraud risks.
- Ongoing monitoring: compliance does not end with the onboarding of a customer. To ensure that a customer remains who they say they are months after onboarding, their data should be subject to ongoing monitoring throughout the whole customer lifecycle.
What Is KYC Remediation?
A lot can change during a customer’s lifecycle. Once you onboard a client, you can never be certain they are still who they say they are a year later. That’s why regulated industries should re-validate their customers. This process is called KYC remediation. It ensures that your customer’s data is updated according to the most recent regulations and your KYC obligations are fulfilled.
Generally, remediation is performed in a 6 or 36-month cycle. It all depends on the client’s risk score. The higher the client’s risk, the shorter the remediation cycle.
KYC Remediation can be a complex and expensive procedure. To make the process easier, start the remediation with only high-risk clients. Firstly, identify the outdated and collect the missing data. Automated KYC software can help you gather this information much faster. Additionally, by enabling constant monitoring of your clients, you’ll know exactly which of them needs to be remediated.
Ondato offers all the necessary KYC and data monitoring tools in one comprehensive suite. Stay compliant with current regulations and mitigate the risk of fraud with our customer data platform.
Who Needs to Perform KYC?
Financial institutions will always be at the centre of KYC, but that doesn’t mean that KYC requirements do not apply to other industries. Knowing who your clients are is not only useful to ensure your company’s integrity and reputation, but can also secure those who shouldn’t be using your service. It is especially true for companies that offer age-restricted services and want to deter minors from using their platform.
Here is a list of the most prominent industries subjected to KYC regulations:
- Finance
- Online gaming
- Gambling
- Alcohol sales
- Travel
- Virtual and Crypto wallets
- Telecommunications services
- Medical services
- Others
Takeaway: Is KYC Only a Legal Requirement?
No. The most important thing to remember about Know Your Customer compliance is that it does more than simply assess money laundering risks. Automated KYC processes help companies protect their reputation, reduce AML compliance costs and ensure a smoother experience for their clients. Choosing a customer identification program like Ondato will make your KYC journey much more efficient.