Watchlist screening has become essential for organisations that wish to meet various legal and financial standards and adhere to Anti-Money Laundering (AML) practices. Watchlist screening involves systematically evaluating individuals, entities, and transactions against predefined, regularly updated lists of interest. This article provides a comprehensive overview of watchlist screening, highlighting its significance in regulatory compliance and detailing the types of lists used to ensure effective screening practices.
What is Watchlist Screening?
Watchlist screening, also sometimes referred to as AML screening, involves the automated, systematic evaluation of individuals, entities, or transactions against predefined lists, commonly referred to as watchlist. These lists include a variety of designations, such as politically exposed persons (PEPs), sanctioned individuals, entities, countries, and those involved in illicit activities.
Why is Watchlist Screening Important?
The primary goal of AML watchlist screening is to identify and examine any connections between a customer or transaction and sanctioned or high-risk entities or individuals. Such connections may indicate an elevated risk profile, requiring further due diligence or additional regulatory action. This rigorous process strengthens organisations’ compliance with regulations like AML and Know Your Customer (KYC) mandates, while also enhancing defences against financial crime, fraud, and illicit activities.
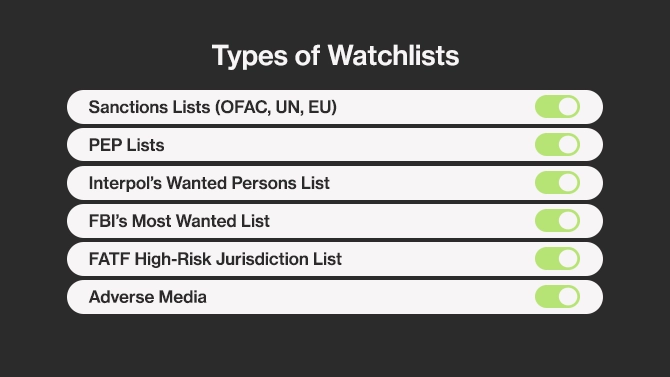
Types of Watchlists
Organisations often need to integrate various lists into their watchlist screening solutions. A list-agnostic capability is crucial for seamless integration and quick availability of these lists for screening and compliance purposes. While many lists are publicly available, solutions that offer native integration with leading data providers ensure fast and reliable access to comprehensive, high-quality data sources.
Here are some of the most common types of watchlists used in robust screening processes:
Sanctions Lists (OFAC, UN, EU)
Sanctions lists maintained by entities like the Office of Foreign Assets Control (OFAC), the United Nations (UN), and the European Union (EU) include individuals, entities, and countries subject to international sanctions for reasons such as geopolitical conflicts, terrorism, human rights abuses, or illicit trade. These lists are updated periodically to reflect changes in global political dynamics, helping organisations comply with international laws and prevent engagement with entities linked to activities against global peace and security.
PEP Lists
PEP lists compile information on individuals who hold or have held prominent public positions. Updated periodically to reflect changes in political positions, these lists are published by various government agencies and international organisations. Screening against PEP lists helps organisations comply with AML and counter-terrorism financing (CTF) regulations, mitigating risks associated with individuals who might exploit their positions for financial gain or illicit activities.
Interpol’s Wanted Persons List
Interpol’s “wanted persons” list contains information on individuals sought by law enforcement agencies worldwide for various criminal activities. Regularly updated, this list enables international law enforcement coordination in locating and apprehending fugitives globally.
FBI’s Most Wanted List
The FBI’s “most wanted” list features individuals wanted for serious crimes in the United States. Updated as needed, this list helps prioritise and focus resources on apprehending high-priority suspects, playing a crucial role in domestic law enforcement efforts.
FATF High-Risk Jurisdiction List
The Financial Action Task Force (FATF) high-risk jurisdictions list assesses the adequacy of AML and CTF measures in various jurisdictions. Updated periodically, this list allows financial institutions to identify and manage risks associated with high-risk jurisdictions, ensuring compliance with international standards.
Adverse Media
Adverse media lists include individuals, entities, or activities flagged in public sources due to associations with negative events, controversies, or illicit behaviour. These lists are vital for risk assessment, providing insights into potential reputational damage and risks. Integrating adverse media lists into the screening process enhances due diligence efforts and helps identify and mitigate potential risks effectively.
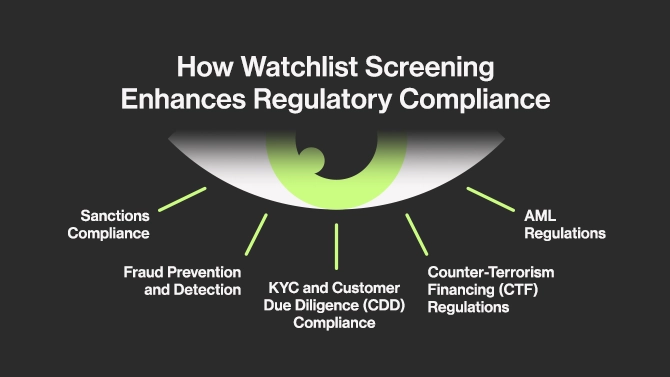
How Watchlist Screening Enhances Regulatory Compliance
Watchlist screening is an integral part of business verification services that help organisations manage compliance risks and meet international regulatory standards. Here’s how watchlist screening supports common regulations:
Sanctions Compliance
Sanctions regulations prohibit business with individuals, entities, or countries subject to economic or trade restrictions. Watchlist screening ensures organisations do not engage with sanctioned parties, maintaining compliance with international sanction laws.
AML Regulations
AML regulations require financial institutions to detect and prevent money laundering activities. AML watchlist screening identifies individuals or entities on government-sanctioned lists or PEP lists, flagging potentially high-risk individuals to prevent the flow of illicit funds.
KYC and Customer Due Diligence (CDD) Compliance
Watchlist screening confirms the legitimacy of customers or business partners, ensuring they are not on restricted lists. This process helps establish the true identity of customers, reducing financial fraud risk and ensuring regulatory compliance.
Counter-Terrorism Financing (CTF) Regulations
CTF regulations aim to prevent funds from supporting terrorism. Watchlist screening identifies individuals or entities associated with terrorism, aiding in detecting and reporting suspicious activities to disrupt potential terrorist financing operations.
Fraud Prevention and Detection
Watchlist screening helps prevent fraud by identifying individuals with a history of fraudulent activities or criminal involvement. Cross-referencing customer data against watchlists detects potentially fraudulent behaviour, allowing organisations to take appropriate action. Additionally, with the use of ongoing monitoring, the process ensures suspicious activity is noticed quickly.
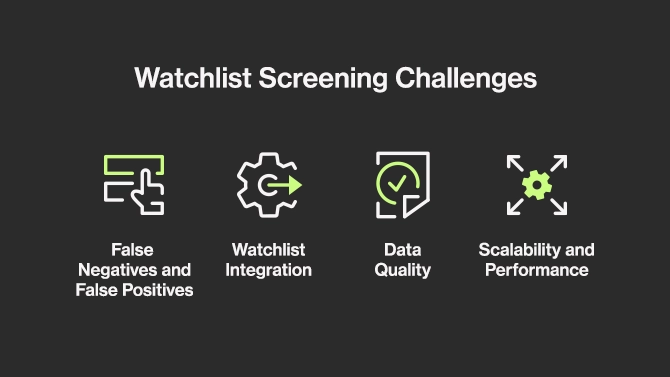
Watchlist Screening Challenges
Despite its importance, watchlist screening presents several challenges. Organisations face complexities in implementing and managing screening processes, including the risk of missing critical matches and dealing with high false positive rates. These challenges highlight the need for precision and efficiency in screening systems, relying on integration, data quality, scalability, and performance capabilities.
False Negatives and False Positives
False negatives occur when the screening algorithm fails to detect a legitimate match due to poor data quality or algorithm configuration. Missing a true hit compromises regulatory compliance and exposes the organisation to legal and reputational risks. Advanced screening algorithms, data quality prioritisation, and comprehensive training programs for analysts are essential to mitigate this challenge.
While false positive rates occur when the screening algorithm generates numerous false alarms. This inefficiency requires significant resources to investigate and clear unnecessary alerts, potentially delaying legitimate transactions or client onboarding as well as upping operational costs. Advanced screening algorithms and customizable tuning parameters are crucial to reduce superfluous alerts and improve operational efficiency.
Watchlist Integration
Integrating global watchlists into a unified screening database can be challenging due to different formats, data structures, and naming conventions. Overcoming this obstacle ensures seamless and effective screening, as discrepancies can lead to missed alerts or false negatives. Technology solutions that standardise watchlist data facilitate immediate and accurate screening.
Data Quality
Maintaining data accuracy and integrity is critical for effective screening. Challenges such as missing data, non-standardized entries, and inconsistent naming conventions can lead to missed alerts. Technology solutions with data cleansing and normalisation capabilities address these issues, ensuring high accuracy and efficacy in the screening process.
Scalability and Performance
Handling high volumes of records is crucial for organisations with extensive customer bases or frequent transactions. Insufficient scalability and performance in screening software can delay processing and hinder timely responses to alerts. Selecting technology solutions with robust scalability and performance capabilities ensures swift and effective screening, even in high-demand environments, providing real-time results.
By addressing these challenges with advanced technology and processes, organisations can enhance their watchlist screening capabilities, ensuring robust regulatory compliance and effective risk management.

Last Thoughts
Watchlist screening is an indispensable tool for organisations committed to maintaining compliance, managing risk, and upholding ethical standards. By understanding its processes, challenges, and importance, businesses can better prepare to navigate the complexities of global regulations and contribute to a safer, more transparent financial system.
Implementing robust watchlist screening practices not only helps organisations avoid legal repercussions but also plays a vital role in the broader fight against financial crimes and terrorism, ultimately contributing to a more secure and trustworthy global economy.
FAQ
Sanctions lists: Lists of individuals, entities, and countries subject to economic or trade sanctions.
Watchlists: Lists of persons or entities that are under scrutiny for potential involvement in illegal activities or that require enhanced due diligence.
PEP (Politically Exposed Persons) lists: Lists of individuals who hold prominent public positions and their relatives and close associates, due to the higher risk of bribery and corruption associated with them.



