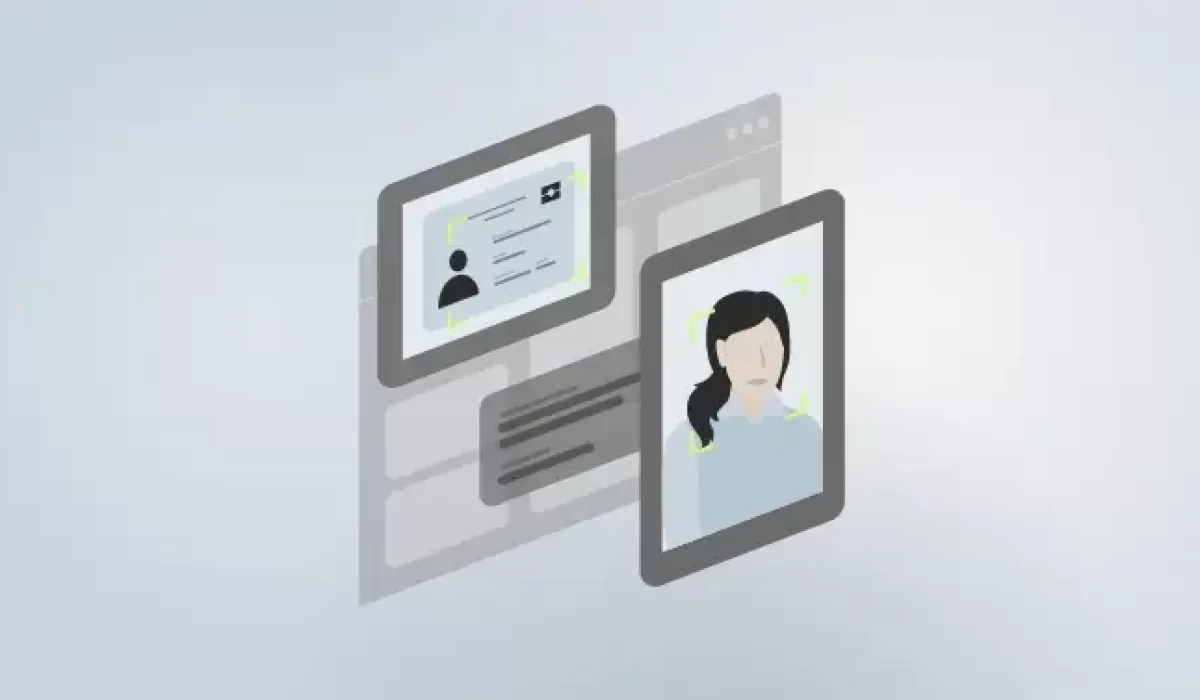
User authentication plays an important role in safeguarding online platforms by verifying users’ identities before granting them access. As data breaches and cyber threats become increasingly common, the need for strong and reliable authentication solutions is more pressing than ever. Organisations face mounting pressure to protect sensitive information and ensure secure online interactions when they authenticate users.
This article explores both traditional and advanced user authentication methods, providing insights for businesses and individuals looking to strengthen their cybersecurity strategies.
The Importance of Authentication
Authentication is the process of verifying a person’s or entity’s identity and determining who gains access to an organization’s resources. As the first line of defence against unauthorised access, it plays a crucial role in platform security. Authentication methods are diverse, each utilizing different techniques to verify the identity of a user or device. This verification is not just a formality; it prevents fraud, ensures compliance with data protection standards, and protects against costly data breaches.
Risks of Weak Authentication
Weak or ineffective authentication can lead to severe security risks, exposing organisations to fraud and unauthorised access to user accounts. The main types of authentication methods include those based on:
- Something users know: Passwords
- Something users have: Tokens
- Something users are: Biometrics
Digital or physical authentication systems ensure the identity verification of users trying to access systems. Understanding these methods can help organizations implement effective security solutions.
Types of Authentication Methods
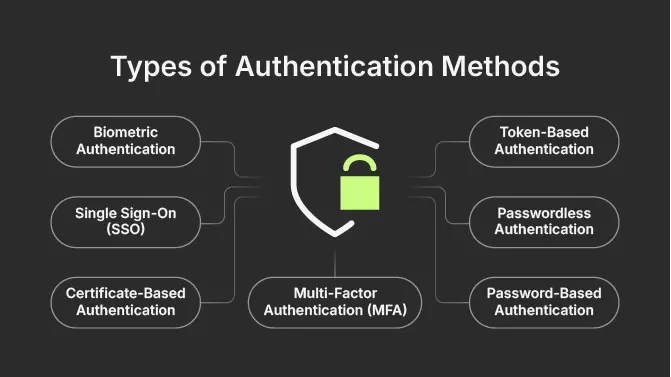
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
MFA is a highly effective security measure that requires users to complete two or more verification steps before gaining access. By combining factors such as passwords, tokens, and biometrics, MFA can block up to 99.9% of automated account takeover attempts.
One of its key benefits is the ability to customise security measures based on user roles or data sensitivity, allowing organizations to tailor their security approach to specific needs. Furthermore, modern MFA solutions seamlessly integrate with existing systems, enhancing security without compromising user experience.
Common methods of MFA include two-factor authentication (2FA), which typically combines a password and an authentication code verification. Push notifications are also widely used, allowing users to quickly approve login attempts via a simple prompt on their smartphone, streamlining the authentication process while maintaining robust security.
Biometric Authentication
Biometric authentication uses unique physical and behavioural traits to verify identity. Fingerprint scanning, known for its 99.9% accuracy, is widely used in smartphones and banking applications. Facial recognition offers hands-free authentication by analyzing features like the distance between the eyes and jaw structure, making it popular for secure payments and device access.
Advanced methods like iris and retina scanning, employed in high-security sectors, analyze eye patterns for verification. Voice recognition authenticates users based on speech patterns and is commonly used in virtual assistants and banking services. Behavioural biometrics, which track interactions like typing speed and gestures, offer continuous security by monitoring user behaviour over time.
Token-Based Authentication
Token-based authentication uses physical or digital tokens to verify user identity, making it a popular choice in corporate environments. One of its key advantages is that it eliminates the need for users to remember complex passwords, significantly reducing the risks associated with password theft. Additionally, this method is scalable, enabling efficient authentication processes as organisations grow. Security measures such as refresh tokens help maintain user sessions without the need for frequent re-authentication, while encryption safeguards tokens against interception and unauthorised use.
Single Sign-On (SSO)
Single Sign-On (SSO) allows users to log in once and gain seamless access to multiple applications using a single set of credentials. This approach significantly enhances user convenience by reducing the number of login attempts required across different services. It also decreases password-related helpdesk requests, freeing IT resources for other tasks. However, implementing SSO can be time-consuming, as setting up and integrating the system demands careful planning and configuration. Despite these challenges, SSO delivers long-term operational efficiency, making it a valuable authentication method for many organizations.
Certificate-Based Authentication
Certificate-based authentication relies on digital certificates derived from cryptographic processes to verify user identities. These certificates, issued and managed by a Certificate Authority (CA), contain identification data, public keys, and digital signatures. For authentication to be successful, users must possess a private key that corresponds to the public key embedded in the certificate. This method is particularly effective in environments where secure access is critical, such as systems involving human users, servers, e-passports, and IoT devices.
Passwordless Authentication
Passwordless authentication removes the reliance on static passwords, instead utilising factors such as email links, unique strings, and biometrics for identity verification. Common methods include facial recognition, fingerprint scanning, proximity badges as physical tokens, and authenticator apps that generate one-time passwords via SMS or mobile applications. Passwordless solutions offer significant benefits, including cost savings and streamlined user management, while enhancing user convenience by eliminating the need for password recall. Examples of passwordless implementations include the Microsoft Authenticator app, which allows identity verification through a mobile device, and FIDO2 security keys that leverage cryptographic techniques for secure and user-friendly access.
Password-Based Authentication
Password-based authentication is the most common method for verifying user identity, relying on a combination of a username and password. Despite its simplicity and widespread adoption, this method has significant security vulnerabilities. Users frequently create weak passwords that follow predictable patterns, increasing the likelihood of being compromised by malicious actors.
Brute-force attacks, which involve automated login attempts using common username and password combinations, are a major security concern. Additionally, credential stuffing attacks exploit users’ tendency to reuse the same credentials across multiple platforms, further amplifying the risk of unauthorized access.
To enhance security, organisations should encourage the creation of strong, complex passwords and implement supplementary security measures such as Multi-Factor Authentication.
Authentication Protocols
Authentication protocols ensure secure communication between clients and servers during the authentication process.
Password Authentication Protocol (PAP)
A basic login process that uses unencrypted usernames and passwords. Its lack of encryption makes it vulnerable to interception.
Challenge Handshake Authentication Protocol (CHAP)
Employs a three-way exchange mechanism for user authentication, enhancing security by avoiding plain-text credential transmission.
JSON Web Token (JWT)
A secure information transfer protocol that is commonly used for API authentication.
- Encodes claims in a header, payload, and digital signature
- Ensures authenticity through digital signatures
Factors to Consider When Choosing an Authentication Method
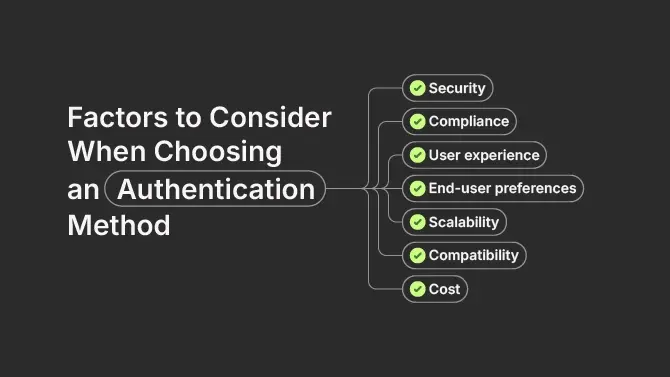
Selecting the appropriate authentication method involves evaluating multiple critical factors to strike a balance between security, usability, and operational efficiency.
Security is the most important, as effective authentication acts as a strong defence against unauthorized access and cyber threats. Strong authentication solutions help prevent breaches and safeguard sensitive information.
Compliance with regulatory frameworks, such as GDPR or industry-specific standards, ensures that sensitive data is handled and protected in accordance with legal obligations.
User experience should be prioritized to streamline account management, minimize the burden of remembering complex passwords, and reduce end users’ frustrations related to logins.
End-user preferences play a crucial role, as familiarity with certain authentication techniques often drives higher adoption rates. Solutions should be user-friendly and adaptable to user behaviour.
Scalability is essential for businesses expecting growth, ensuring the authentication system can handle increased traffic and evolving security needs without compromising performance.
Compatibility with existing technology stacks prevents conflicts and ensures seamless integration with current systems and protocols, reducing implementation challenges.
Cost considerations are equally important, factoring in expenses related to implementation, maintenance, and the need for supporting systems such as recovery tools or fraud prevention mechanisms. Evaluating these factors helps businesses choose a method that aligns with their specific security, operational, and financial goals.
Why Ondato is a Good Tool for Authentication
Comprehensive identity verification solutions: Ondato offers a wide range of verification methods, including biometric authentication, document scanning, and face recognition. These tools help ensure that only verified users gain access to systems, reducing the risk of fraud and unauthorized access.
Biometric authentication for enhanced security: With Ondato’s biometric solutions, organizations can verify user identities using unique traits like facial features or voice recognition. Biometric data is harder to forge than traditional credentials, providing a strong layer of security while streamlining the login process.
Seamless integration: Ondato integrates effortlessly with existing platforms and systems, from mobile apps to enterprise software, without disrupting operations.
Compliance and data security: Ondato ensures compliance with regulations such as GDPR, AML (Anti-Money Laundering), and KYC (Know Your Customer) requirements.
User-friendly experience: Ondato simplifies the verification process, making it quick and easy for users to complete identity checks.
Fraud prevention and risk management: AI-driven fraud detection systems proactively monitor for suspicious patterns, offering real-time risk management.

Last Thoughts
Understanding and choosing the right authentication method is crucial for securing digital environments. From traditional password-based methods to advanced biometric and passwordless options, each has its strengths and weaknesses. Multi-Factor Authentication and Single Sign-On provide additional layers of security and convenience, while certificate-based and token-based methods offer robust solutions for specific scenarios.
Ultimately, the choice of authentication method should be guided by security needs, user experience, scalability, and compliance requirements. By carefully considering these factors, organizations can implement effective and secure authentication systems that protect their digital assets and user data.



