In today’s interconnected world, where digital interactions have become an integral part of our lives, securing our online identities is of incredible importance. With the rise of cyber threats and identity theft incidents, traditional password-based authentication systems have proven to be increasingly vulnerable. The job of protecting users falls on the shoulders of many businesses. Thankfully, technology has advanced to provide a stronger defence mechanism known as Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA). In this blog post, we will explore the concept of multi-factor authentication and its significance in bolstering digital security.
Multi-factor Authentication Explained
Multi-factor authentication, sometimes referred to as risk-based authentication, is a security mechanism that combines multiple independent factors to verify a user’s identity. It offers an additional layer of protection beyond the traditional username and password combination, making it considerably more challenging for unauthorised individuals to gain access to sensitive information. It is commonly used by financial institutions but is a good practice for any business dealing with clients.
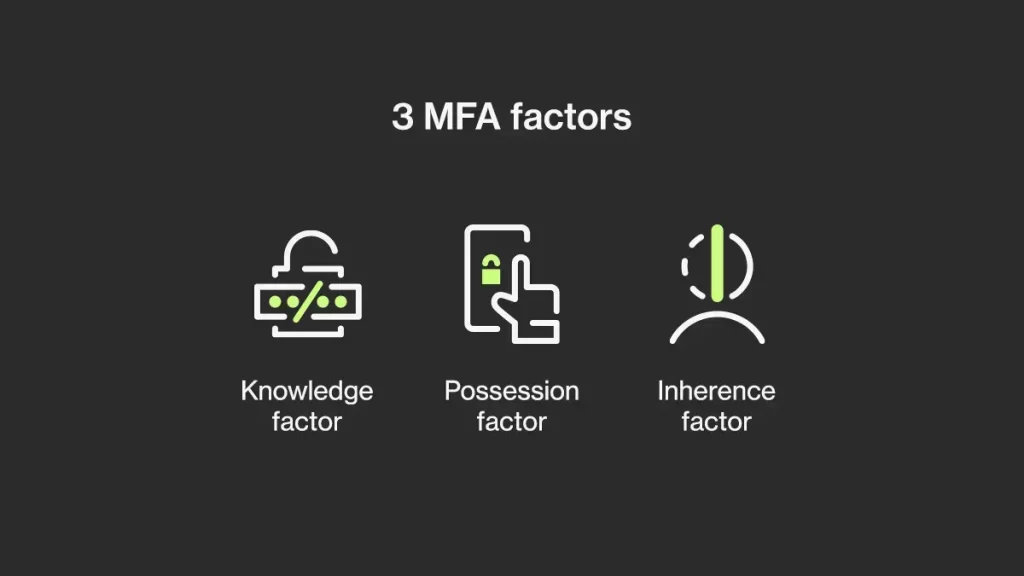
MFA operates on the principle of “something you know, something you have, and something you are.” These multiple authentication factors typically fall into three categories:
- Knowledge Factor: This includes something the user knows, such as a password, a PIN, or the answer to a security question. It serves as the first line of defence and is often the most familiar form of authentication.
- Possession Factor: These involve something the user possesses, such as a physical token, an access card, or a smartphone. These items generate a unique one-time password (OTP) that is time-sensitive and can only be used for a limited period.
- Inherence Factor: These factors are based on a unique physical characteristic of the user, such as fingerprint, facial recognition, or retinal scan. Authentication using biometrics is considered the standard due to its reliability and ease of use.
Why are Biometrics Considered the Safest Authentication Method?
Many businesses, especially financial institutions that require a higher level of security, have implemented biometric authentication for their MFA. This is due to the fact it is by far the safest and most convenient method.
Passwords, pins or security questions can often be forgotten, causing issues for the user. As we know, in fear of that happening, users also often write down this information. A sticky note with a password can often be lost or get into the hands of the wrong person. Alternatively, in order not to forget them, many users use very simple passwords or the same password for every account, which makes them much easier to guess for hackers.
Physical security tokens, access cards and even mobile phones can be lost, damaged or forgotten somewhere, keeping the user from logging in whenever they need to. They can also be stolen and used by fraudsters.
Biometrics, though, will not be forgotten in the car or left in the office, they do not need to be written down on post-it notes. This makes biometric authentication the most convenient and secure way to access online services.
Why is MFA Important?
- Additional Security: By incorporating multiple factors, MFA significantly reduces the chances of unauthorised access. Even if one factor is compromised, the attacker would still need to bypass the additional layers of authentication, which adds a substantial barrier to entry.
- Defense Against Credential Theft: Password breaches and phishing attacks are common tactics employed by cybercriminals to steal sensitive information. MFA acts as an effective deterrent against these threats since it requires additional verification beyond the stolen credentials.
- User Convenience: While security is paramount, user experience also plays a crucial role. MFA offers a balance between security and convenience by providing various authentication methods to suit individual preferences. Users can choose from a range of options, including SMS codes, authentication apps, or biometric scans. It also allows users to gain remote access to online accounts, which makes their experience with a service much more convenient.
- Compliance with Regulatory Standards: Many industries and organizations are subject to stringent security regulations that require robust authentication measures. MFA assists in meeting these requirements by adding an extra layer of security, ensuring compliance with data protection standards.
How does Multi-factor Authentication Work?
Multi-factor authentication works by requesting multiple forms of ID from the user at the time of account registration. The system stores this ID and user information to allow the user to gain access to the service at the next login. The login is a multi-step process that verifies the other ID information along with the password.
Registration
A user creates the account with a username and password. They then link other items, such as a mobile device for SMS verification or physical hardware to their account. The item might also be virtual, such as an email address, mobile number, or authenticator app code. All these items help to uniquely identify the user and should not be shared with others.
Authentication
Upon the next login, the user is prompted to provide the same information, be it physical tokens, biometric data or randomly generated codes from apps like Microsoft authenticator. The authentication system then confirms that the data matches and allows the user to access the service.
The Pros and Cons of MFA
One of the biggest shortcomings of traditional user ID and password logins is that passwords can be easily compromised, exposing sensitive data to hackers. Brute-force attacks are also a real threat, as bad actors can use automated password-cracking tools to guess usernames and passwords until they find the right sequence. This makes non-MFA authentication methods too simple. Multi-factor authentication, on the other hand, can help reduce security risks. However, just like anything else, multi-factor authentication technology comes with its own pros and cons:
Pros
- adds layers of security at the hardware, software and personal ID levels;
- can use OTPs sent to phones that are randomly generated in real-time and, therefore, harder for hackers to break;
- can reduce security breaches by up to 99.9% over passwords alone;
- makes user authentication easier and more accessible;
- enables businesses to opt to restrict access for the time of day or location;
- has scalable costs and can be adapted to the company.
Cons
- a phone is needed to get a text message code;
- physical tokens can get lost or stolen;
- mobile devices can get lost or stolen;
- MFA verification can fail if there is a network or internet outage;
- MFA techniques must constantly be upgraded to protect against criminals who work incessantly to break them.
Outro
In an era where cyber threats continue to evolve, adopting Multi-Factor Authentication is a crucial step towards securing our digital identities. By combining multiple independent factors, MFA provides a robust defence mechanism against unauthorised access and identity theft. As individuals and organisations embrace this enhanced security measure, we can foster a safer digital ecosystem that empowers users to confidently navigate the online world. Remember, when it comes to protecting our digital lives, it’s always better to be safe than sorry, and Multi-Factor Authentication paves the way for a more secure future.