Data security has come a long way since the inception of passwords and knowledge-based authentication. Due to the constantly growing risk of spoofing, changing data protection regulations, and company policies, old security measures are no longer viable. Thus, data security experts are implementing newer and better options, such as various biometric authentication methods.
Today, biometrics is one of the most secure methods to safeguard digital information from unauthorized access. Users can use biometrics for user login, access control, and other applications that require verification of the user’s identity. Every biometric authentication method is designed to be easy to use while delivering high levels of security by ensuring that the person using a device or system is who they say they are.
What Is Biometric Authentication?
Biometric authentication is a security method that identifies a person during the enrollment phase by analyzing and comparing their unique physical or behavioral characteristics. The most significant benefit of biometrics is its ability to quickly and reliably verify returning clients. Since biometric data is unique to each individual, it is a secure alternative to pin codes, passwords, and knowledge-based authentication.
How Does Biometric Authentication Work?
The first step of biometric authentication is to map out the data of the selected biometric trait. Eligible biometric traits involve several different parts of the human body, such as the iris, voice, gait, fingerprints, and many other unique attributes.
The biometric system then stores collected data in the database. When prompted, the system compares the stored biometric characteristics with the new sample. If it finds a match, the user is successfully authenticated.
Most commonly, biometrics are used for identification and authentication purposes. During biometric identification, the technology confirms whether the person attempting access is actually who they claim to be (for example when allowing someone into a building). In authentication mode, biometrics confirm whether the user has permission to perform a specific operation (such as logging into an account).
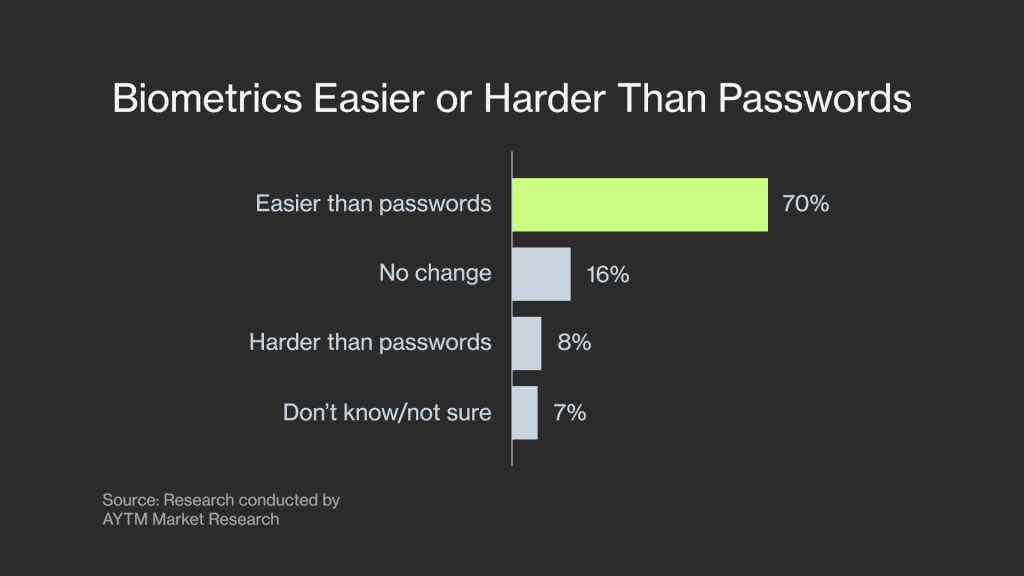
Even though several decades ago, biometrics seemed more like science fiction than reality, now it is widely accepted and implemented. According to a survey by Visa, 70% of consumers believe that biometrics are easier, and 46% think they are more secure than a password or PIN code. As a result, the preference for biometric authentication is growing.
Who Uses Biometric Authentication?
Biometrics is a convenient way to authorize access to assets or services. The security method has these common use cases:
- Access control
- Online browsing control
- Preventing fraud
- User authentication
- Presence control
- Payment method
Due to its wide range of uses, biometric security benefits many industries, including government agencies, healthcare providers, retailers, hotel chains, and airlines. For example, the military uses biometrics for security purposes on military installations; it also allows soldiers to speed up the security process by using their fingerprints instead of ID cards when entering buildings or going through security checkpoints.
Biometric technology is becoming increasingly prevalent, thus its applications are growing. Here are some common examples:
- Border control and immigration. The US border control subjects arriving and exiting individuals to a biometric screening. It allows CBP officers to identify national security threats and visa overstays.
- Law enforcement. Police officers frequently use biometrics to aid criminal investigations. For example, biometric facial identifiers are especially valuable for locating people on watchlists and establishing identities in situations where a person cannot identify themselves.
- Airport security. Many major airports have been using biometrics to verify passenger identity. It helps to speed up self check in time and results in a better passenger boarding experience.
- Access to mobile devices and authentication. When electronic identification is necessary, biometric technology adds another layer of security to the process.
- Banking. Anti-Money Laundering and Know Your Customer regulations require strong and secure client identification and authentication solutions. By implementing biometric security, banks can prevent fraud, such as identity theft or spoofing.
- Internet of Things. Many smart devices use some type of biometrics. For instance, home assistants employ voice as a biometric identifier.
What Are the Types of Biometric Authentication Methods?
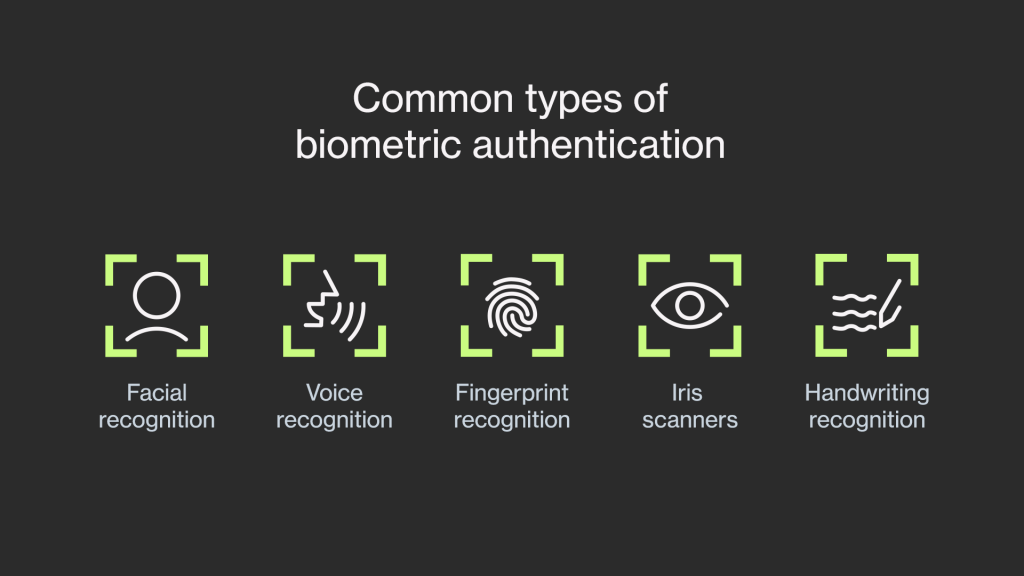
Biometric security systems, also known as modalities, are built to recognize different biometric traits during authentication. Each biometric system involves unique biological and behavioral aspects. The biometric traits implemented in a system have an effect on its performance. Thus it’s important to get familiar with the most common types.
Face
The human face is one of the commonly used biometric traits. The authentication is facilitated with static or video face images. During the process, AI maps out a person’s facial features, such as the location, shape, and spatial relationships of their eyes, nose, lips, and so on. The technology determines if two different photos represent the same person and helps locate a face among a large collection of existing images.
Benefits of Facial Recognition
Facial recognition systems have the edge over other types of biometrics. When paired with liveness detection, thermal imagery, and other technology, this biometric modality demonstrates a highest level of security.
Face recognition technology allows the detection of various spoof artifacts, such as screens, photos, masks, etc, making the process a fast and efficient way to authenticate returning users.
Additionally, facial recognition is very easy to use. Since cameras have become a big part of our lives, this biometric modality can be implemented with the help of a user’s phone. For this reason, the face is the most preferred biometric trait for authentication.
Common Challenges of Facial Recognition
There are several issues users may encounter during facial recognition-based authentication. The first one is the unsuitable background of the video or an image. A complex background can make a person’s face indistinguishable, preventing successful authentication. Another challenge is lighting. Poor illumination can fail the process. It’s also worth noting that a face can change drastically over time. Common factors include aging, cosmetic surgery, accidents, and illness.
Voice
Voice is a biometric attribute that combines both biological and behavioral traits. The sound of a person’s voice is determined by many physical characteristics, such as the size and shape of their mouth, tongue, nose, or vocal cords. It can also be significantly affected by their language, medical issues, or emotions.
Voice or speaker recognition identifies a person based on their voice. It works by assigning a speaker simple speaking tasks to create a unique profile of their voice. The system then cross-matches the profile with new voice samples used to authenticate the speaker.
Benefits of Voice Recognition
A person’s voice is unique and extremely hard to falsify. Additionally, voice recognition is simple to implement. Users are not required to possess any additional devices and typically use their phones.
Common Challenges of Voice Recognition
There are some important factors that can make a speaker recognition system fail. Any respiratory illness, such as a common cold, can easily alter the user’s voice preventing the authentication. Background noise may also interfere with the process.
Fingerprints
Fingerprints are no longer used exclusively in forensics. These days, most people use fingerprint biometrics. Since it can be easily implemented in any device, such as a mobile phone or a laptop, owners can use their fingerprint to get safe access to their devices.
Benefits of Fingerprint Recognition
The most significant advantage of fingerprint scanning is that fingerprints are unique to each individual. Even twins have different fingerprint ridges and patterns..
Another benefit is the ease of use and accessibility. Even though they are widely implemented and commonly used in consumer devices, from door locks to laptops, a standalone fingerprint scanner is easy to obtain, too.
Common Challenges of Fingerprint Recognition
Despite its benefits, fingerprint-based authentication systems have downsides. Fraudsters have devised ways to falsify fingerprints and use them for illicit activities. While the process of bypassing fingerprint-based security is challenging, it’s possible with enough effort. Also it is possible to perform unauthorized authentication while a person is asleep or unconscious.
Iris
Iris, a colored, circular membrane surrounding the pupil of the human eye is another unique trait. The complex structure of the iris is extremely hard to replicate. Thus it is also used in biometric systems.
Benefits of Iris Recognition
Iris is an externally visible organ that is well protected from injuries. It is easy to access and set up for authentication. Additionally, changing pupil size can be beneficial for ensuring liveness.
Challenges of Iris Recognition
Despite its benefits, the iris scanners are still a developing technology. Even though it seems promising, current systems have a high false non-match rate (FNMR).
Handwriting
Similarly to optical character recognition (OCR), handwriting recognition is capable of using pattern matching for converting handwritten letters into computer text. However, handwriting is more or less unique to a person, so it can also be used as a behavioral biometric system.
The technology can be static or dynamic. The static process simply compares the handwriting. On the other hand, the dynamic process analyzes stroke, pen pressure, shape writing speed, and several other characteristics to verify a user’s identity. If the text is imputed digitally, typing recognition aids the process.
Benefits of Handwriting Recognition
Handwriting recognition is simple to understand and intuitive enough for users. When the process is dynamic, the possibility of falsified handwriting is minimized, increasing its security.
Challenges of Handwriting Recognition
While our handwriting is unique, it’s also highly inconsistent. Many factors can lead to change in a person’s writing; the most common examples are stress, fatigue, emotional state, or injury. For this reason, handwriting provides low-level security.
Which Type of Biometric Authentication Is Best?
As you can see, each biometric authentication method varies in its applications and security.
However, this does not mean that the less secure options are useless. It all comes down to the purpose and usability. For example, replacing voice recognition with facial recognition in a home assistant would prevent the ability for them to give commands. On the other hand, facial recognition technology, implemented into a banking app can help to quickly and securely authenticate a client.
What is Liveness Detection?
Biometric systems often employ additional technology to improve security. The most common choice is liveness detection.
Liveness detection is a process of verifying that a person is alive by using their body parts as an identifier. For example, the technology can verify that a person has placed a finger on an infrared sensor. During an iris scan,this technology looks for the movement in a person’s eye. When paired with facial recognition-based biometrics modality, liveness is detected by asking a person to perform simple movements to ensure an authentic presence.
By ensuring liveness, companies can prevent identity theft or fraud. The technology can also be used to verify the authenticity of identification documents, effectively detecting spoofing and alterations.
How Does Ondato Biometric Authentication Work?
Ondato knows how important customer authentication experience is in the strict regulatory environment. A solution that does not effectively satisfy the needs of customers, can result in bad business outcomes. Thus we strive to ensure the high usability of our biometric authentication.
Ondato employs the most effective and comfortable biometrics trait – the human face. The biometric authentication process begins at the client’s onboarding. First, the system scans a customer’s face creating a 3D map. The scan is paired with liveness detection, which ensures that a person is truly present during the process. Then, the data is saved and encrypted.
When a returning customer wants to access the service, their face is scanned again. Our system compares it with the previously collected data and scans for possible spoofing methods and other alterations.
Only if the face is an absolute match, the customer’s identity is confirmed, and they receive access to the service.
Ondato’s biometric authentication keeps an accuracy of 1 in 12,800,000 at less than 1% False Reject Rate (FRR). The process is also very swift – taking only milliseconds to complete.
Why Should You Implement Facial Biometrics Scanning into Your Services
Many experts believe that biometrics will eventually replace traditional security methods, such as passwords. Let’s take a look at the advantages that facial biometric scans provide.
Biometric Authentication Is Faster than Other Methods
Speed is an important factor in facilitating a satisfactory customer experience. That’s why a long and complicated authentication process may discourage clients from using your services. For this reason, Ondato biometric authentication takes milliseconds.
Biometric Authentication Improves User Experience
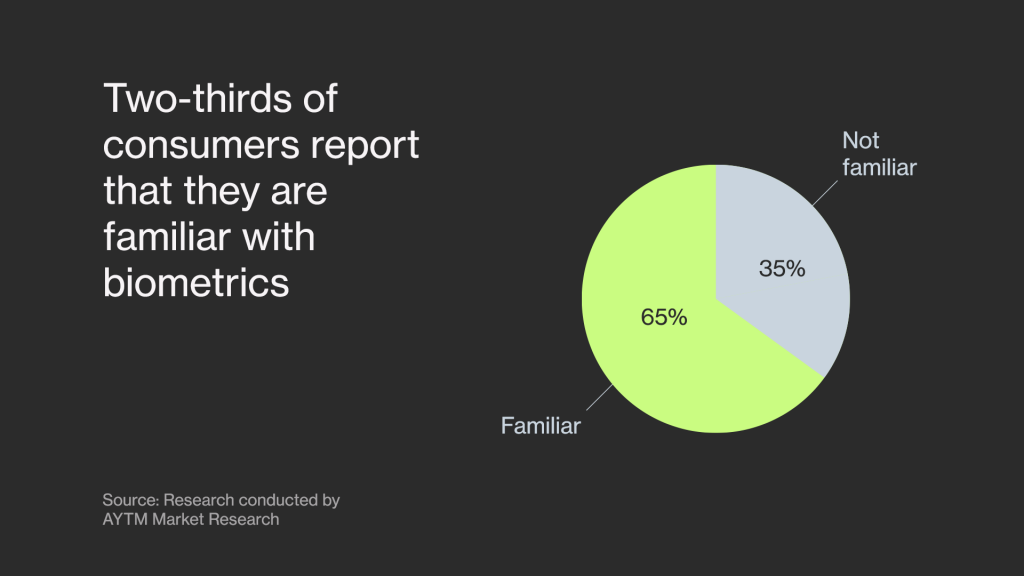
A survey has shown that over 65% of customers are familiar with biometrics. Most people are already used to the process, especially when it comes to facial recognition technology.
Biometric security methods don’t require much effort from your client – all they have to do is pose for their smartphone or webcam for a few seconds, and they are good to go. That’s why implementing it into your service can boost user experience.
Biometric Authentication Keeps Fraudsters at Bay
While no current technology is 100% safe from fraudsters, biometrics is a tough method to beat. Enriched with spoofing and liveness checks deters fraudsters by making the process much more challenging than stealing a password.
Traditional Authentication Methods Aren’t Trustworthy
Passwords remain the most common authentication method, but they are vulnerable to various cyberattacks, such as phishing. Verizon Data Breach Investigations Report showed that 81% of hacking-related breaches used stolen and/or weak passwords.
Other methods, such as document and token authentication, require a document, token, or a similar device to receive access. This type of authentication poses usability challenges and opens the possibility of fraud if a person loses their document or token.
Meanwhile, knowledge-based authentication is even more unsafe. It involves common questions, such as the client’s mother’s maiden name or the name of their childhood pet. It has been reported that many users thoughtlessly share answers to these questions on social media.
Conclusion
Biometrics are the future of authentication. The technology offers a more secure, convenient, and cost-effective method for verifying identities. Biometric systems have many advantages over traditional password-based systems. It provides a higher level of security as it cannot be stolen or forgotten like passwords, making it more difficult for hackers to gain access. Biometrics also reduces the risk of identity theft in combination with other security measures such as two-factor authentication and encryption.